Boost Your Productivity: The Ultimate List of Habits for Software Engineers
In today's fast-paced and competitive world, productivity has become more important than ever. With the constant barrage of distractions and demands on our time, it can be difficult to stay focused and make the most of our limited resources. However, by adopting the right tools and strategies, we can increase our productivity and achieve more with less effort.
In this article, I am going to summarize tools and techniques that worked for me at different periods of my life. The idea of the the article is to keep short and comprehensive list of efficient productivity techniques.
Productivity is not a one-size-fits-all concept and what works for one person may not work for another. To maximize productivity, try out different methods and identify what works best for you according to your strengths, weaknesses, and personal preferences.
Goal Setting
Setting goals is like having a map to guide you towards success. It helps you focus your efforts and resources towards what really matters, and don't waste on something that doesn't. With clear and specific goals, you can increase your motivation and sense of accomplishment. It's like having a superpower that can help you achieve more with less effort, and stay on track towards your dreams. So go ahead, set those goals, and unleash your inner superhero!
SMART Goals

SMART goals are a specific type of goal-setting framework that can help create more effective goals. SMART is an acronym that stands for:
Specific: Goals should be clear, defining exactly what needs to be accomplished.
Measurable: Goals should be measurable, so that progress can be tracked and evaluated.
Achievable: Goals should be challenging but realistic, taking into account available resources and capabilities.
Relevant: Goals should be relevant to the broader objectives and priorities.
Time-bound: Goals should have a clear timeline for completion.
HARD Goals
HARD stands for heartfelt, animated, required and difficult. They each mean:
Heartfelt: If you want to learn a new skill, imagine the joy of having a new skill. Then, connect that joy with the goal and use that emotion as your motivation for learning.
Animated: Visualize what achieving your goal would look like. Incorporate every sense you can and imagine what it would sound, feel, smell or even taste like so you can remember the feeling every time you think about your goal.
Required: Connect your goal to something that's necessary for you. For example, if you want to improve your research skills, volunteer to create a report for your team, as this obligation can motivate you to keep working on your goal.
Difficult: Set a goal that challenges you. By doing this, you'll feel proud when you complete it.
Write Down
Writing down goals helps to make them more specific and tangible. When we write down our goals, we are forced to articulate them in a clear way, which makes them easier to remember and focus on.
Secondly, writing down goals helps to increase accountability. When we have written goals, we are more likely to take them seriously and work towards them consistently, rather than letting them become vague or forgotten over time. We are also more likely to take action to overcome obstacles or setbacks.
Thirdly, writing down goals helps to track progress and evaluate success. When we have clear goals and a written record of our progress, we can see how far we have come and identify areas where we may need to adjust our approach or strategy. This can help us to make more informed decisions and take action to improve our performance.
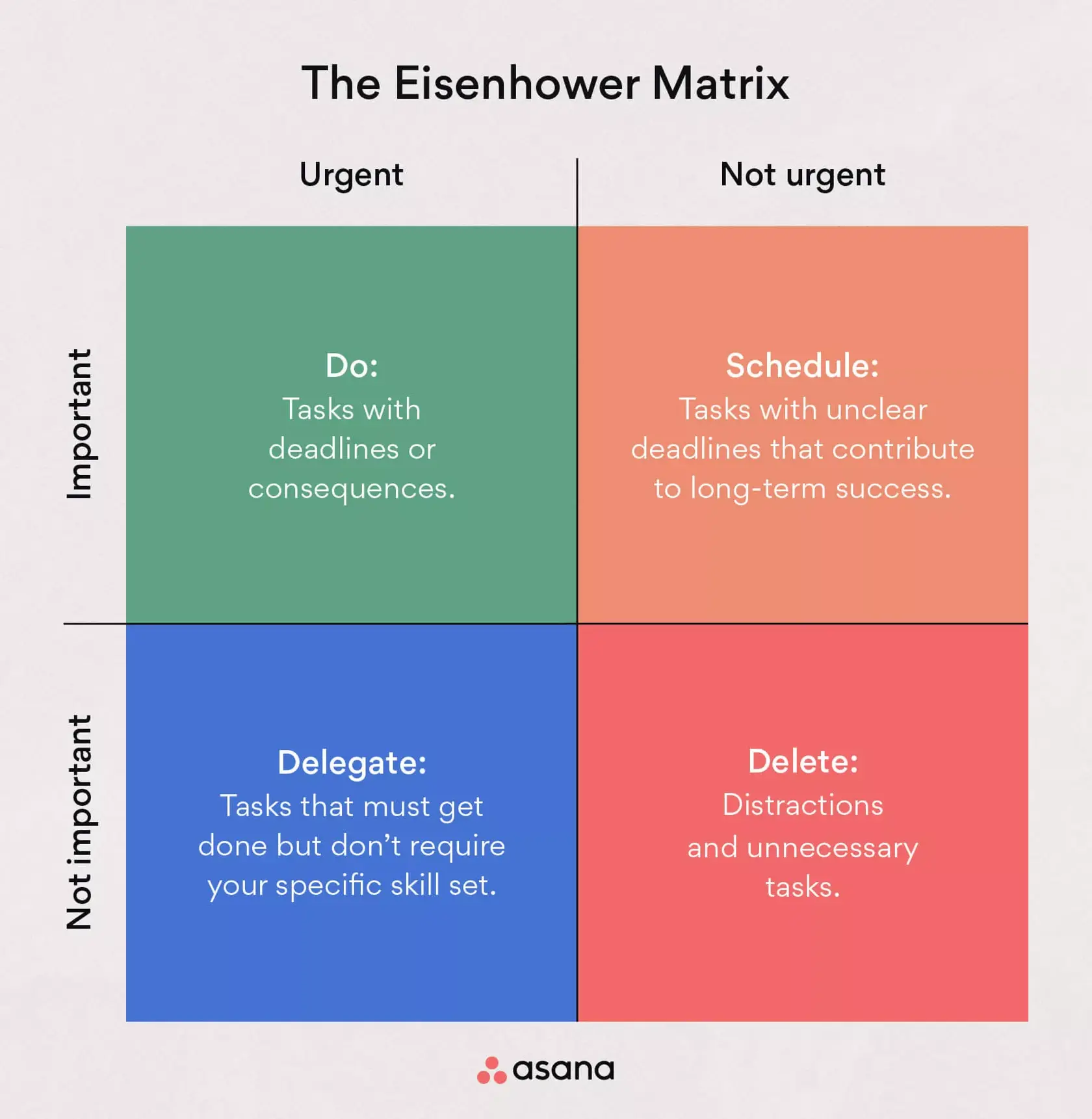
Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Urgent-Important Matrix, is a productivity tool that helps prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance. It involves categorizing tasks into four quadrants based on whether they are urgent, important, both, or neither, and then taking action accordingly.
Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule )
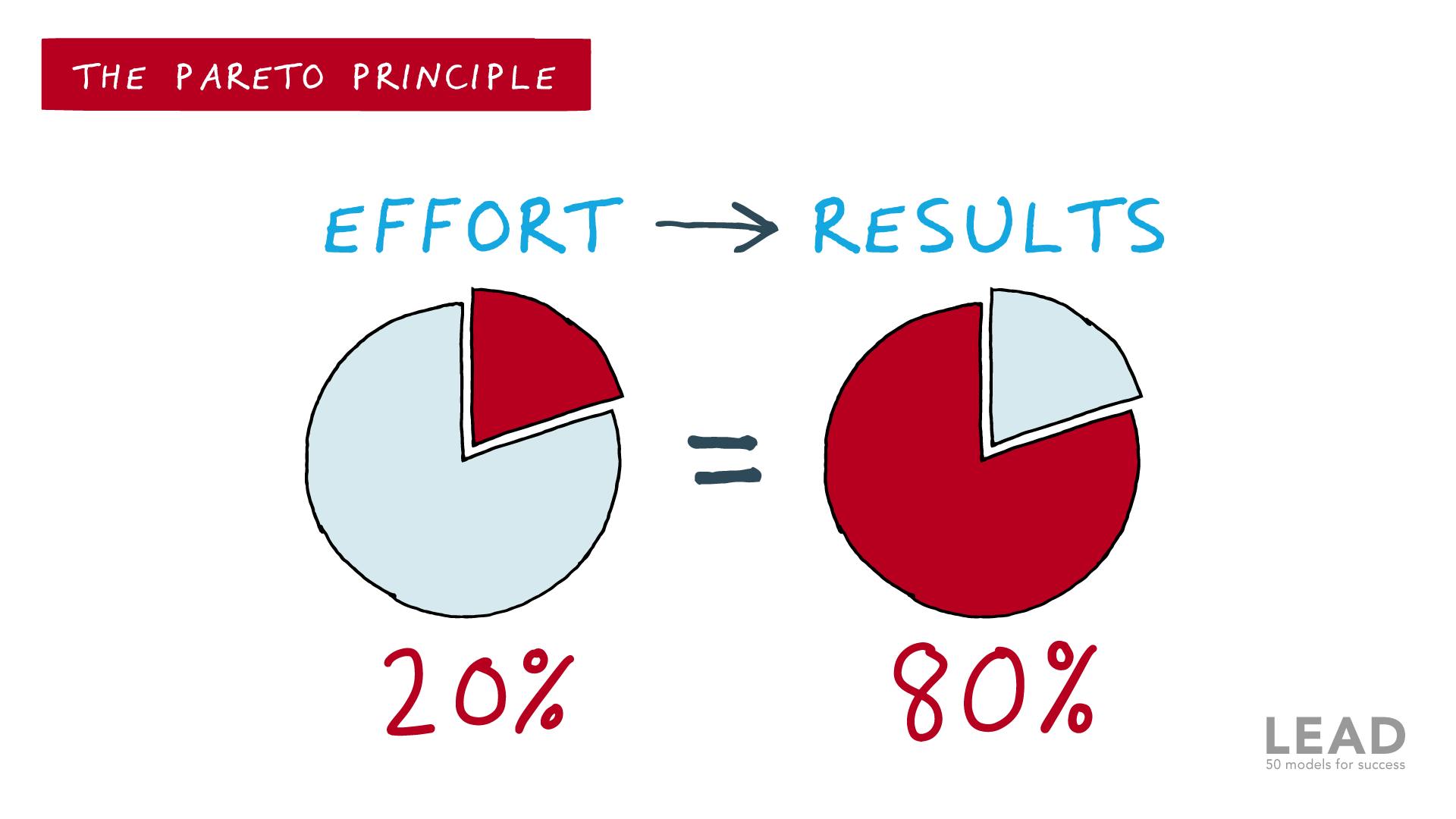
The Pareto Principle, also known as the 80/20 rule, is a concept that suggests that roughly 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes.
To use the Pareto Principle for goal setting, you can start by identifying the few key activities or tasks that will have the greatest impact on your desired outcomes. This might involve identifying the 20% of actions that will yield 80% of the results you are looking for.
Once you have identified those key activities, you can focus your time and energy on them.
The Ivy Lee Method
The Ivy Lee Method is a productivity strategy that was developed by a business consultant named Ivy Lee in the early 1900s. It involves the following steps:
At the end of each workday, write down the six most important tasks to be completed the following day.
Prioritize these tasks in order of importance.
The next day, focus on the first task and work on it until it is completed before moving on to the next task.
Repeat this process for each task on the list until all tasks are completed.
Warren Buffet's 25-5 Rule
Warren Buffet's 25-5 Rule is a goal-setting strategy that helps to prioritize goals and focus on what is most important. The rule involves the following steps:
Write down your top 25 goals.
Review your list and circle the five goals that are most important to you.
Focus your time and energy on the top five goals and set aside the other 20 goals for later consideration.
Avoid working on any of the other 20 goals until you have made significant progress on your top five goals.
The 5 Whys
The "Why" method is a powerful tool for goal setting that involves asking a series of "why" questions to uncover the underlying motivations and values behind a goal. To use the "Why" method for goal setting, follow these steps:
Identify a specific goal that you want to achieve.
Ask yourself why this goal is important to you. Write down your answer.
Ask yourself why again, based on your previous answer. Write down your answer.
Repeat this process several times, continuing to ask "why" based on each previous answer, until you have uncovered the deeper motivations and values that underlie your goal.
Use this information to refine your goal, and to ensure that it is aligned with your core values and motivations.
WOOP Method
WOOP is a goal-setting framework developed by psychologist Gabrielle Oettingen. It stands for Wish, Outcome, Obstacle, and Plan, and is a four-step process for setting and achieving goals. Here is how it works:
Wish: Identify a specific and meaningful wish or goal that you want to achieve. This should be something that is important to you and aligns with your values.
Outcome: Visualize the desired outcome or result of achieving the wish or goal. This should be a positive and vivid mental image that inspires you.
Obstacle: Identify the obstacles or barriers that stand in the way of achieving the goal. These may be internal, such as limiting beliefs or fears, or external, such as lack of resources or support.
Plan: Develop a specific and actionable plan for overcoming the obstacles and achieving the goal. This may involve identifying specific actions, resources, or support that you need to achieve the goal.
Time Management
Time management is the secret sauce to unlocking productivity potential. By juggling priorities like a pro, you can focus on the tasks that truly matter, navigating your way to success with clear goals in sight. As you become a time-management maestro, stress dwindles, decision-making sharpens, and procrastination withers away. Efficiency reigns supreme, fostering a collaborative environment for personal growth, and paving the way for a harmonious work-life symphony. So, embrace time management and let the productivity party begin!
Time-boxing
Time-boxing, also known as time-blocking, is a time management technique that involves allocating specific blocks of time to individual tasks or activities. Time boxing encourages you to work within a fixed time frame, which can lead to a better sense of urgency and efficiency.
Here's how to implement time-boxing:
Identify the tasks you need to complete.
Estimate how much each task will take.
Create a schedule, dividing your day into blocks of time dedicated to specific tasks.
Assign each task to a time block, ensuring you include breaks and buffer time for unexpected events.
Begin working on your tasks, focusing on one time block at a time.
When the allocated time for a task is up, move on to the next task or time block, even if the current task is not completed.
Review your progress and adjust your time estimates as needed.
Time boxing helps to increase focus, maintain momentum and prevent procrastination. By setting clear boundaries for each task you can better manage your time and workload.
Use Deadlines
A deadline is a specific date or time by which a task, project, or assignment must be completed. Here are a few reasons why deadlines are so effective:
They create a sense of urgency: Knowing that a deadline is approaching can motivate us to work harder and faster. This can help us avoid procrastination and stay on track.
They help us prioritize: Deadlines force us to prioritize our work and focus on the most important tasks first. This can help us use our time more effectively.
They provide accountability: When we set a deadline, we are making a commitment to ourselves or to others.
To use deadlines effectively, here are a few tips:
Set realistic deadlines: Make sure that the deadline you set is realistic and achievable. If you set a deadline that is too tight, you may end up feeling overwhelmed and stressed.
Break tasks into smaller deadlines: Instead of setting one big deadline for a project, break it down into smaller tasks with their own deadlines. This can help you stay on track and ensure that you make progress every day.
Use a calendar or project management tool: this can help you visualize your progress.
Review and adjust deadlines as needed: If you find that you are consistently missing deadlines, take a step back and re-evaluate your approach. You may need to adjust your workflow to better suit your needs.
Parkinson's Law
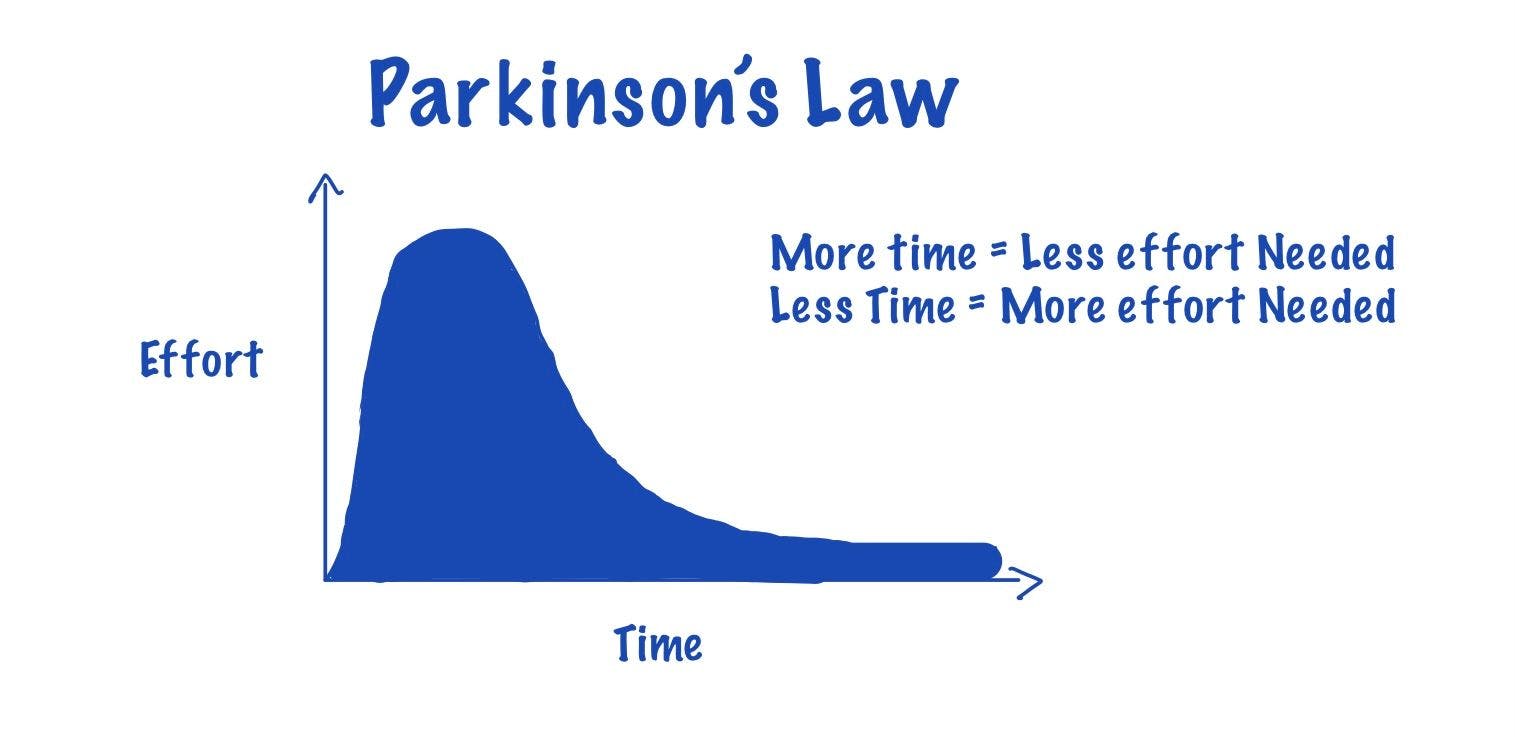
Parkinson's Law suggests that people tend to take the entire time allotted for a task, whatever the actual amount of work required is. Consequently, if a task is given more time than necessary, individuals may become less efficient, spending the extra time on unnecessary details or procrastinating.
To counteract Parkinson's Law and improve time management, it is helpful to set shorter, more focused deadlines. By creating a sense of urgency and limiting the time available for a task, individuals are often more productive and efficient in completing their work.
Batch Processing
Batch processing in time management is a technique where similar tasks are grouped together and completed in a single block of time. This approach allows to focus on one type at a time, reducing the efforts required to switch between different tasks.
Pomodoro Technique
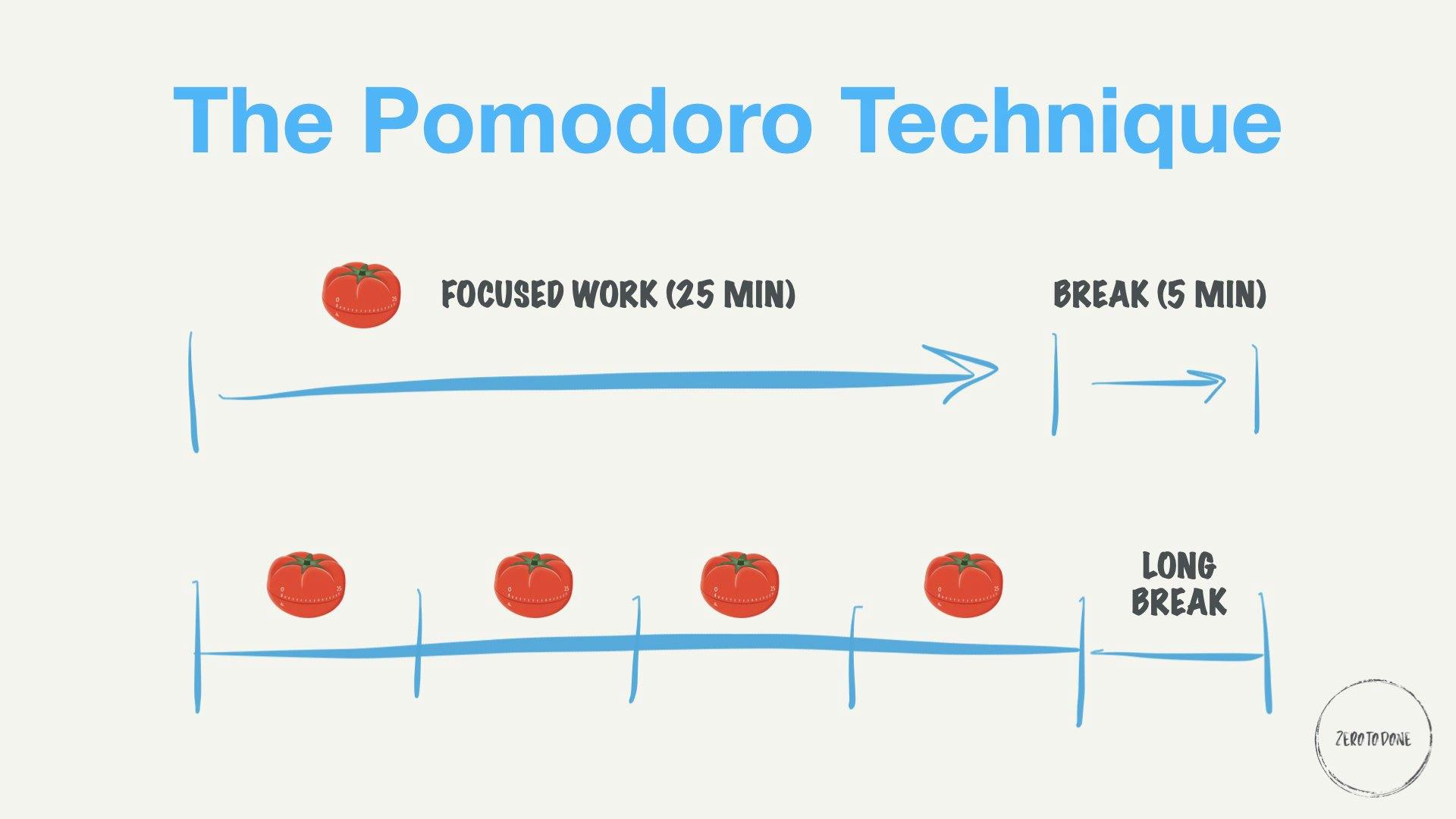
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method developed by Francesco Cirillo in the late 1980s. The technique aims to improve productivity and focus by breaking work into short, concentrated intervals, separated by brief breaks. The name "Pomodoro" comes from the Italian word for tomato, inspired by the tomato-shaped kitchen timer Cirillo used when developing the technique.
Here's how the Pomodoro Technique works:
Choose the task you want to work on.
Set a timer for 25 minutes (1 Pomodoro).
Work on the task until the timer goes off.
Take a short break (usually around 5 minutes).
After completing four Pomodoros, take a longer break (15-30 minutes).
2-Minute Rule
The 2-Minute Rule is a simple time-management strategy that helps with overcoming procrastination. It was popularized by David Allen in his book "Getting Things Done," where he suggests that if a task can be completed in two minutes or less, it should be done immediately rather than being postponed or added to a to-do list.
The 2-Minute Rule is based on the idea that it often takes more time and energy to organize and schedule a task than it does to complete it. By doing small tasks immediately, you prevent them from piling up and becoming a source of stress. Additionally, the sense of accomplishment from completing small tasks can provide momentum to tackle more significant tasks.
The 2-Minute Rule can also be adapted as a starting point for larger tasks. When facing a big task, commit to working on it for just two minutes. Often, this small commitment can help overcome the initial resistance to starting, and once the task has been initiated, it's easier to continue working on it beyond the initial two minutes.
Time Audit
A time audit is a productivity technique that involves analyzing how you spend your time during a given period, such as a day or a week. The purpose of a time audit is to identify areas where you can improve your time management, increase your productivity, and ensure that your daily activities align with your priorities and goals.
To conduct a time audit, follow these steps:
Choose a period for the audit: Decide whether you want to track your time for a day, a week, or even a month. A week is often a good starting point, as it gives a more comprehensive view of your habits and routines.
Record your activities: Throughout the chosen period, keep a log of your activities. You can use a pen and paper, a spreadsheet, or a time-tracking app to record the start and end times for each task or activity you engage in. Be as detailed and accurate as possible.
Categorize your tasks: Once you have collected your data, group your tasks into categories. These categories may include work, leisure, sleep, exercise, chores, etc.
Analyze your time usage: Calculate the total time you spent on each category during the audit period.
Evaluate and adjust: Compare your time allocation with your priorities and goals. Identify areas where you're spending too much or too little time and consider making adjustments to better align your time usage with your objectives. This may involve cutting down on certain activities, delegating tasks, or finding ways to use your time more efficiently.
By regularly conducting time audits, you can gain valuable insights into your time management habits and make adjustments to improve your productivity and overall well-being.
Focus
Imagine you're trying to juggle a dozen balls at once - it's chaotic, stressful, and almost guaranteed to end in disaster. The same is true when it comes to trying to juggle multiple tasks at once. Without focus, our productivity suffers as we struggle to manage competing demands for our attention. By zoning in on a single task, we can eliminate distractions and channel all of our energy and effort towards achieving our goals.
Single Task
Focusing on a single task at a time is generally considered to be good for productivity.
When you focus on a single task, you are less likely to get distracted by other tasks, notifications, or interruptions. This helps you maintain your concentration and stay on track.
As well, focusing on a single task at a time allows you to make the most of your time and mental resources.
Workspace
The workspace you create can have a significant impact on your productivity. A well-designed workspace can help you stay organized, reduce distractions, and create a more comfortable and efficient environment for work. Here are a few reasons why workspace is important:
Organization: A clean and organized workspace can help you stay focused and reduce mental clutter. Make sure your desk is free of unnecessary items and that everything you need is within easy reach.
Comfort: Physical discomfort can be a major distraction and drain on productivity. Invest in an ergonomic chair, adjust your desk height, and ensure that your computer screen is positioned at a comfortable height to reduce eye strain.
Lighting: Good lighting is crucial for reducing eye strain and staying alert. Try to position your workspace near a natural light source, or invest in a high-quality desk lamp.
Noise: Noise can be a major distraction, so try to create a workspace that is as quiet as possible. Use noise-cancelling headphones or a white noise machine to block out distracting sounds.
Personalization: Personalizing your workspace can help create a sense of ownership and increase motivation. Add a few personal touches, such as a favorite plant, photo, or piece of art.
By taking these factors into consideration, you can create a workspace that is optimized for productivity and helps you do your best work.
Deep Work

The Deep Work technique is a productivity concept introduced by Cal Newport in his book "Deep Work: Rules for Focused Success in a Distracted World." It refers to the practice of dedicating uninterrupted, focused time to perform complex, cognitively demanding tasks that require deep concentration.
The main principles of Deep Work technique are:
Schedule blocks of time: Set aside dedicated time slots for deep work activities, free from distractions and interruptions.
Eliminate distractions: Remove potential distractions, such as social media, email, and other notifications, to maintain focus on the task at hand.
Create routines and rituals: Develop routines that signal the beginning and end of deep work sessions, making it easier to transition into a focused state.
Prioritize high-value tasks: Focus on tasks that make a significant impact on your work or personal development, and avoid shallow, low-value tasks.
Set clear goals: Define the objectives of your deep work session to ensure you maintain focus and make meaningful progress.
Minimalism
Minimalism can be a powerful tool for improving productivity, as it helps to eliminate distractions, reduce decision fatigue, and create a more focused and intentional environment. Here are some tips on how to use minimalism to improve productivity:
Streamline your workspace: Create a clean, clutter-free workspace by eliminating unnecessary items and organizing your essentials. This can help reduce visual distractions and create a more calming environment.
Simplify your schedule: Prioritize your most important tasks and eliminate unnecessary meetings or commitments. This can help you focus on what really matters and avoid feeling overwhelmed.
Reduce digital distractions: Turn off notifications, delete unnecessary apps, and limit your time on social media. This can help you stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked.
Create a minimalist routine: Establish a simple and consistent routine for your day, such as a morning ritual or a daily to-do list. This can help you stay on track and avoid decision fatigue.
Focus on quality over quantity: Rather than trying to do everything, focus on doing a few things well. This can help you produce higher quality work and avoid burnout.
By simplifying your environment and mindset, you can create a more efficient and productive workflow, leading to better outcomes and greater success.
Physical Care
Picture this: you're trying to run a marathon, but your shoes are too tight, your water bottle is empty, and your legs feel like lead. It's no surprise that your performance suffers, and you struggle to reach the finish line. The same is true for productivity - without taking care of our physical condition, we can find ourselves struggling to keep up with the demands of work. By prioritizing our physical health and wellness, we can boost our energy, focus and perform at our best. After all, a healthy body is the foundation for a productive mind.
Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is important for productivity because of its impact on cognitive function and overall well-being. Some reasons why hydration is crucial for productivity include:
Improved cognitive function: Proper hydration is essential for maintaining optimal brain function. Dehydration can impair concentration, memory, and overall cognitive performance.
Increased energy levels: Water is necessary for maintaining energy levels. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, which negatively affects focus and motivation.
Reduced headaches: Dehydration is a common cause of headaches. Staying hydrated helps prevent these issues.
Enhanced mood: Hydration has been linked to improved mood and emotional stability.
Better physical performance: Proper hydration supports muscle function, temperature regulation, and overall physical performance, allowing you to be more active and engaged throughout the day.
To stay hydrated, aim to drink water regularly throughout the day, even before you feel thirsty. Keep a water bottle nearby as a reminder, and consider incorporating water-rich foods such as fruits and vegetables into your diet to help maintain optimal hydration and support productivity.
Eat Properly
Proper eating is important for productivity because it provides the necessary nutrients and energy for optimal cognitive function, physical well-being, and mood regulation. Here are some best eating tips to support productivity:
Balanced meals: Consume meals that include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals to maintain energy levels and brain function.
Regular eating intervals: Eat at regular intervals throughout the day to maintain consistent blood sugar levels and prevent energy crashes.
Mindful eating: Avoid overeating or eating too fast. Focus on your meal and eat slowly to improve digestion and prevent post-meal sluggishness.
Limit sugar intake: Excessive sugar consumption can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, leading to energy fluctuations and decreased productivity. Opt for natural sources of sugar, like fruits, when craving something sweet.
Healthy snacks: Choose nutrient-dense snacks like nuts, seeds, yogurt, and whole-grain products to fuel your brain and maintain energy levels between meals.
Stay hydrated: Drink water regularly to support optimal cognitive function, mood, and energy levels.
Limit caffeine: While caffeine can provide a temporary boost, overconsumption can lead to energy crashes and disrupted sleep. Moderate your caffeine intake and avoid it late in the day.
Breakfast matters: Start your day with a nutritious breakfast to support energy levels, cognitive function, and overall productivity.
Meal planning: Plan your meals in advance to ensure you consistently eat a balanced diet and reduce the temptation of unhealthy choices.
Listen to your body: Pay attention to your body's hunger and satiety signals. Eat when you're hungry and stop when you're full to maintain optimal energy levels and prevent overeating.
By following these eating tips and maintaining a balanced diet, you can support cognitive function, mood, and energy levels, ultimately enhancing productivity and work performance.
Sleep
Sleeping is essential for productivity because it plays a crucial role in various cognitive and physiological processes. Here are some reasons why sleep is vital for productivity:
Memory consolidation: Sleep helps solidify and consolidate new information and memories, improving learning and retention.
Cognitive function: Adequate sleep supports optimal cognitive function, including attention, problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity, all of which are critical for productivity.
Emotional regulation: Sleep is essential for regulating emotions and maintaining a positive mood, which contributes to a better work environment and increased motivation.
Physical health: Sleep helps restore and repair the body, supporting overall physical health and energy levels.
Immune function: Sufficient sleep strengthens the immune system, reducing the risk of illness and maintaining productivity.
Stress reduction: Sleep helps reduce stress levels and manage anxiety, allowing for better focus and mental clarity during work hours.
Mental stamina: A well-rested brain can maintain focus and perform tasks more efficiently, reducing the likelihood of errors and increasing productivity.
Rejuvenation: Sleep provides a necessary break for the brain and body to recover from daily activities, helping to maintain optimal function and prevent burnout.
To support productivity, aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Develop a consistent sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure your sleep environment is comfortable and conducive to rest. Prioritizing sleep will positively impact cognitive function, mood, and overall well-being, ultimately enhancing productivity and work performance.
Exercise
Exercising is important for productivity due to its positive effects on mental, emotional, and physical health. Here are some reasons why exercise is beneficial for productivity:
Cognitive function: Exercise stimulates the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports neuronal growth and enhances cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and problem-solving.
Energy levels: Regular physical activity increases blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain, resulting in higher energy levels and better focus throughout the day.
Stress reduction: Exercise helps reduce stress by releasing endorphins and lowering cortisol levels, contributing to better mental clarity and focus.
Emotional well-being: Physical activity is known to improve mood, reduce anxiety, and boost self-esteem, leading to a more positive and motivated work environment.
Sleep quality: Regular exercise helps regulate sleep patterns, ensuring better quality sleep and the restoration of cognitive and physical functions.
Physical health: Exercise enhances overall physical health by strengthening the immune system, reducing the risk of illness, and increasing stamina, all of which support productivity.
Time management: Engaging in physical activity can lead to better time management skills, as it requires discipline and planning to incorporate exercise into daily routines.
Creativity boost: Exercise can help foster creative thinking by providing a break from work tasks, allowing the mind to wander and generate new ideas.
To support productivity, aim to include regular physical activity in your routine. Choose activities you enjoy, and consider scheduling exercise before work hours to kickstart your day with increased alertness and energy.
Mental Care
Imagine you're trying to solve a complex puzzle, but your mind feels foggy and distracted. It's hard to focus, and you keep making mistakes. The same is true for productivity - without taking care of our mental condition, we can find ourselves struggling to stay focused and engaged in our work. By prioritizing our mental health and wellness, we can boost our creativity, problem-solving abilities, and resilience, and unlock our full potential. After all, a healthy mind is the key to unlocking a productive and fulfilling life.
Mindfulness
Mindfulness is important for productivity because it trains the mind to stay present and focused, which enhances cognitive function and emotional well-being. Mindfulness also fosters creativity and resilience, allowing individuals to approach work tasks with a clear and calm mindset, even in the face of challenges.
To get started with mindfulness to increase productivity, follow these steps:
Set your intention: Determine your motivation for practicing mindfulness and how it will support your productivity goals.
Start small: Start with short mindfulness exercises, like 5-10 minutes of guided meditation or deep breathing, to build a habit and gradually increase your practice over time.
Find a quiet space: Choose a quiet space free from distractions, where you can focus on your mindfulness practice without interruption.
Use guided meditations: Use guided meditations or mindfulness apps to help you get started and maintain focus during your practice.
Focus on the present moment: During mindfulness practice, focus on the present moment, using techniques like deep breathing, body scanning, or mindful observation to bring yourself into the present moment and quiet the mind.
Be consistent: Make mindfulness a consistent practice, incorporating it into your daily routine to build a habit and reap the full benefits of the practice.
Be patient: Remember that mindfulness is a practice, and it takes time and patience to develop the skill and see the benefits. Don't get discouraged if you don't see immediate results.
Gradually integrate mindfulness into your workday: Once you feel comfortable with your mindfulness practice, start integrating it into your workday by taking short mindfulness breaks or using mindfulness techniques to refocus during tasks.
Practice mindfulness outside of work: Practice mindfulness outside of work, like during exercise or other activities, to maintain a consistent practice and support overall well-being.
By following these steps, you can develop a mindfulness practice that supports your productivity goals and enhances your overall well-being.
Gratitude
Gratitude is important for productivity because it helps cultivate a positive mindset, increases motivation, and fosters strong relationships. When we practice gratitude, we focus on what we have instead of what they lack, leading to improved well-being and productivity. Here are some ways to practice gratitude:
Keep a gratitude journal: Write down three things you're grateful for each day to reflect on the positive aspects of your life.
Express gratitude to others: Show appreciation to colleagues or loved ones by thanking them for their support or help.
Practice gratitude meditation: During meditation, focus on what you're thankful for and visualize the positive aspects of your life.
Write gratitude letters: Write letters to people who have positively impacted your life and express your appreciation for their support.
Focus on the present moment: Practice mindfulness and focus on the present moment, taking time to appreciate the positive aspects of your surroundings.
By incorporating gratitude into your daily routine, you can cultivate a positive mindset, improve motivation, and enhance relationships with colleagues and loved ones.
Positive Thinking
When we practice positive thinking, we focus on solutions instead of problems, leading to greater productivity and success. Here are some ways to practice positive thinking:
Practice self-affirmations: Use positive affirmations to remind yourself of your strengths and capabilities.
Reframe negative thoughts: Reframe negative thoughts into positive ones by looking for the positive aspects of a situation.
Visualize success: Visualize yourself successfully completing tasks and achieving your goals.
Focus on solutions: When faced with a challenge, focus on finding solutions instead of dwelling on the problem.
Use positive self-talk: Use positive self-talk to stay motivated and maintain a positive mindset.
Surround yourself with positivity: Surround yourself with positive people and influences to reinforce positive thinking.
Learn from mistakes: Instead of dwelling on mistakes, use them as learning opportunities to improve and grow.
Celebrate successes: Celebrate your successes, no matter how small, to reinforce positive thinking.
Stoicism
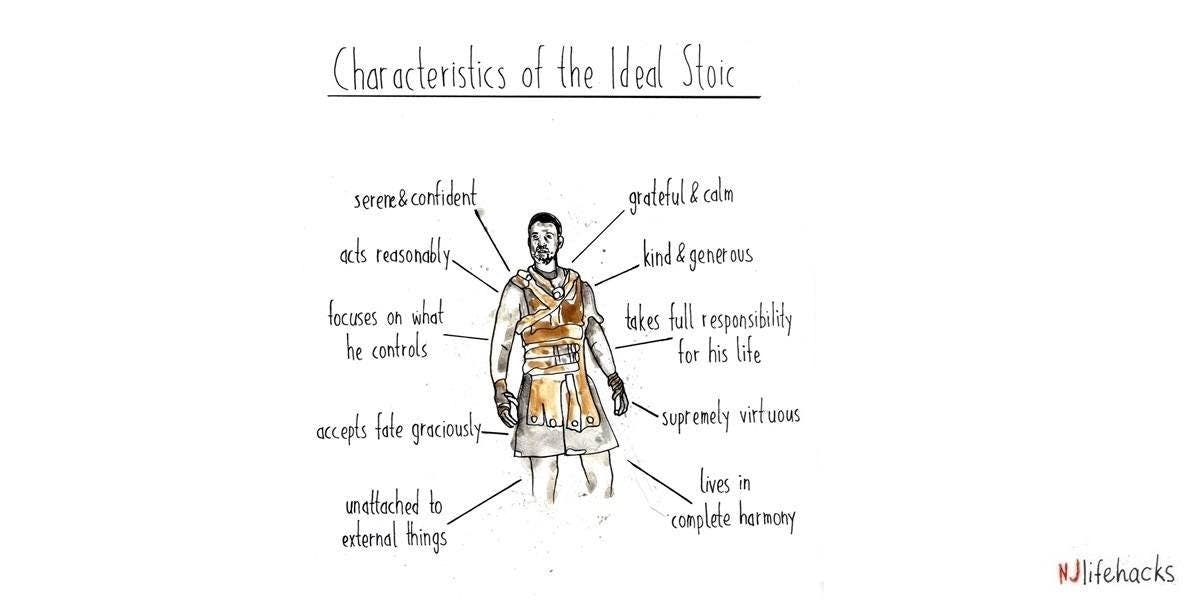
Stoicism is important for productivity because it cultivates a mindset of resilience, self-discipline, and mental toughness. Stoicism teaches us to focus on what we can control, let go of what we cannot, and to approach challenges with a rational and objective mindset. Here are some ways to get started with Stoicism:
Read Stoic philosophy: Read works by Stoic philosophers such as Seneca, Epictetus, and Marcus Aurelius to gain a deeper understanding of Stoic principles.
Focus on what you can control: Instead of focusing on external factors that are beyond your control, focus on what you can control, such as your thoughts, actions, and attitude.
Practice self-discipline: Develop self-discipline through practices such as setting goals, prioritizing tasks, and following through on commitments.
Accept challenges: Embrace challenges as opportunities for growth and learning, and approach them with a rational and objective mindset.
Let go of negative emotions: Let go of negative emotions such as anger, fear, and anxiety, and focus on rational and objective thinking.
Practice gratitude: Cultivate gratitude for what you have and the opportunities presented to you, even during challenging times.
Take responsibility: Take responsibility for your thoughts, actions, and decisions, and avoid blaming external factors for your circumstances.
By incorporating Stoic principles into daily life, we can develop a resilient mindset, stay focused, and maintain productivity during challenging times.
Motivation
When we are motivated, we have a sense of purpose and direction, which leads to increased focus, efficiency, and productivity. Here are some ways to practice motivation:
Set goals: Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals to provide direction and motivation.
Find purpose: Identify your personal and professional purpose to stay motivated and engaged in your work.
Celebrate small wins: Celebrate small successes to reinforce motivation and maintain a positive mindset.
Practice positive self-talk: Use positive affirmations and self-talk to maintain motivation and a positive mindset.
Create a supportive environment: Surround yourself with positive influences and support to maintain motivation and focus.
Break tasks into smaller parts: Break larger tasks into smaller, more manageable parts to stay motivated and avoid feeling overwhelmed.
Use incentives: Use incentives or rewards to stay motivated and reinforce positive behavior.
Visualize success: Visualize yourself successfully completing tasks and achieving your goals to maintain motivation and focus.
Stay accountable: Hold yourself accountable for your goals and tasks to maintain motivation and follow-through.
Practice self-care: Prioritize self-care activities, such as exercise, adequate sleep, and healthy eating, to maintain motivation and overall well-being.
Productivity Systems
Think of productivity as a puzzle, with each task representing a piece that needs to fit together seamlessly to create a complete picture. Without a clear plan or system in place, it can be difficult to fit all the pieces together in a way that makes sense. That's where productivity systems come in - they provide a framework for organizing your tasks and maximizing your efficiency, so you can focus on what really matters. By using a productivity system, you can streamline your workflow, reduce decision fatigue, and achieve more in less time. After all, when it comes to productivity, having a system in place can be the difference between chaos and success.
Getting Things Done (GTD)
The Getting Things Done (GTD) system is a productivity methodology created by David Allen. It's a framework that helps individuals organize their tasks and projects in a way that maximizes their productivity and reduces stress.
The GTD system is based on the idea that people can achieve more by clearing their minds of all the tasks and projects that they need to do and organizing them into a system that they can trust. The system is made up of five key steps:
Capture: Write down all the tasks, ideas, and projects that come to your mind, using any tool or method that works for you (e.g. paper, digital notes, voice memos, etc.)
Clarify: Process the items you've captured and decide what you need to do with each of them. Decide if an item is actionable or not, and if it is, determine what the next action should be.
Organize: Put the actionable items into a system that you trust and that makes sense to you. This could be a to-do list, a task manager app, a calendar, or a combination of these.
Reflect: Review your lists regularly to make sure that you're on track and that you're not forgetting anything important. Also, use this time to make adjustments and to reprioritize tasks as needed.
Engage: Finally, engage in the tasks and projects that you've identified, and focus on completing them one at a time.
The GTD system is designed to help individuals become more organized, focused, and productive. By following these five steps, people can reduce the mental burden of keeping track of all the things they need to do and focus their energy on completing the tasks that are most important.
Zen To Done (ZTD)
Zen To Done (ZTD) is a productivity system created by Leo Babauta that is heavily inspired by the principles of Zen Buddhism. It's a simple and flexible system that is designed to help individuals develop productive habits and achieve their goals.
The Zen To Done system is made up of ten habits that are grouped into four key areas:
Collect: This involves capturing all the tasks, ideas, and commitments that come to your mind, and keeping them in a central location that you trust. This could be a notebook, a digital tool, or a combination of both.
Process: This involves going through your collection system regularly and deciding what needs to be done with each item. You can use the 2-minute rule to quickly complete any tasks that can be done in two minutes or less. For more complex tasks, you can break them down into smaller steps and schedule them into your calendar or task list.
Plan: This involves setting goals and creating a plan of action to achieve them. You can use a simple system like the MIT (Most Important Task) method to prioritize your tasks and focus on the most important ones.
Do: This involves taking action on your tasks and projects, and developing the habit of completing them on a regular basis. You can use the Pomodoro technique to work in short, focused bursts and take breaks in between.
The Zen To Done system emphasizes simplicity, flexibility, and mindfulness. It encourages individuals to focus on one habit at a time and to build upon their successes gradually. By developing these habits, people can become more organized, productive, and fulfilled in their personal and professional lives.
The Agile Results Method
The Agile Results Method is a productivity system that combines principles from agile software development and personal productivity to help individuals achieve their goals more efficiently and effectively. It was developed by J.D. Meier, a former program manager at Microsoft.
The Agile Results Method is based on three core principles: results, principles, and practices.
Results: The system emphasizes setting clear goals and outcomes, and breaking them down into small, actionable steps that can be completed within a short period of time. This helps individuals focus on what's important and avoid getting overwhelmed by a long to-do list.
Principles: The system is based on a set of guiding principles that help individuals make better decisions and achieve their goals more effectively. These principles include things like "think big, act small," which encourages individuals to set ambitious goals but break them down into small, manageable steps. Another principle is "batch your work," which suggests grouping similar tasks together to increase efficiency.
Practices: The system includes a set of practices that help individuals implement the principles and achieve their desired results. These practices include things like timeboxing, which involves setting a fixed amount of time to work on a task and then taking a break. Another practice is scheduling, which involves allocating specific times for tasks and prioritizing them based on their importance and urgency.
The Agile Results Method is a flexible system that can be customized to fit the unique needs and preferences of each individual. It emphasizes continuous improvement and encourages individuals to experiment with different practices and principles to find what works best for them.
Overall, the Agile Results Method is a great option for those who want a flexible and effective productivity system that is based on proven principles and practices. It can help individuals stay focused, motivated, and on track to achieving their goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, productivity is a crucial component in achieving personal and professional success.
However, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Every individual has unique strengths, weaknesses, and circumstances that affect their ability to be productive. The journey towards productivity requires self-awareness, experimentation, and a willingness to adapt and learn. By utilizing goal-setting tools, time management techniques, and physical and mental wellness strategies, we can optimize our productivity and achieve our desired outcomes. Remember, the path to productivity is not a destination, but a continuous journey of growth and improvement. So embrace your individuality, explore what works for you, and keep striving towards your goals.